Fatty liver disease is a health condition affecting millions of people worldwide. Fatty liver disease can happen to anyone, regardless of weight, age, or lifestyle. It is a silent disease that often goes undetected until it reaches advanced stages. The good news is that it is a preventable and curable condition.
What is Fatty Liver(Steatosis)
A fatty liver also called hepatic steatosis is a condition in which an excessive amount of fat accumulates in the liver. Normally liver has a small amount of fat stored and the problem arises when this storage exceeds 5% to 10% of liver weight.
The function of the Liver:
- Filtration of Blood: The liver filters blood to remove toxins and waste products from the body.
- Production of Bile: Bile, produced by the liver, helps break down fats in the small intestine.
- Excretion of Substances: The liver excretes excess bilirubin, cholesterol, hormones, and drugs from the body.
- Metabolism of Nutrients: The liver helps in the metabolism of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates to provide energy for the body.
- Storage of Nutrients: The liver stores glycogen, vitamins, iron, and minerals to be used by the body as needed.
- Synthesis of Proteins: The liver synthesizes plasma proteins, such as albumin and clotting factors, that are important for maintaining overall health.
Causes and Risk Factors of Fatty Liver:
- Obesity: Excessive fat accumulation in the liver due to overeating, particularly refined carbohydrates, and sugars, can lead to fatty liver disease.
- High Blood Fat Levels: High levels of triglycerides or LDL cholesterol in the blood can also contribute to developing fatty liver disease.
- Diabetes or Pre-Diabetes: Insulin resistance, a precursor to diabetes, can cause fat to build up in the liver.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension can damage the liver and contribute to the development of fatty liver disease.
- Unhealthy Diet: Consuming a diet high in refined and processed foods, particularly those found in the middle aisles of supermarkets, can lead to fatty liver disease.
- Menopausal women are found prone to this condition.
- Patient with obstructive sleep apnea is found to be associated with this condition.
- Hispanic or Asian descent are found more prone to fatty liver.
- Taking certain medicines like (amiodarone, diltiazem, and tamoxifen.)
Symptoms of Fatty Liver
Mostly asymptomatic, commonly noticeable symptoms, if occur, are:
- The stomach is bigger than it should be ( large belly fat).
- Have a hard time losing weight,
- Experience chronic abdominal issues, pain abdomen, or sensation of fullness in the right upper abdomen.
- Feeling tired and exhausted, nausea, appetite, or weight loss.
- Yellowish discoloration of skin and eyes.
- Edema of leg and abdomen.
- Pruritis which means itching over the whole body due to increased bilirubin.
It’s essential to take action to improve your liver health to prevent further damage and potentially reverse the condition.
General Terms
What is Steatosis:
Simple fat accumulation without any inflammation in the liver is called steatosis.
What is steatohepatitis:
When fat accumulation causes inflammation and swelling this condition is called steatohepatitis.
What is NASH:(Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis)
It is the inflammation of the liver owing to causes other than alcohol intake.
What is NAFLD:( NON-alcoholic fatty liver disease)
It is a type of fatty liver disease from causes other than alcohol intake.
Types
There are two primary types of fatty liver disease:
- alcohol-induced
- non-alcohol-related fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Alcohol-induced fatty liver disease
Alcohol-induced fatty liver disease develops due to excessive(heavy) alcohol consumption. Consuming one drink per day for women and two for men is considered moderate. It’s estimated that around 5% of people in the United States have alcohol-induced fatty liver disease.
Non-alcohol-related fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
It affects individuals who do not consume excessive amounts of alcohol. This condition affects approximately one in three adults and one in 10 children in the United States. While the exact cause of NAFLD is not known, researchers have identified several risk factors such as obesity and diabetes that can increase the likelihood of developing the condition. Moreover, the incidence is rising because of processed foods, especially junk food intake and processed carbohydrates, and many more.
Although both conditions have different causes, they can have similar effects on the liver.
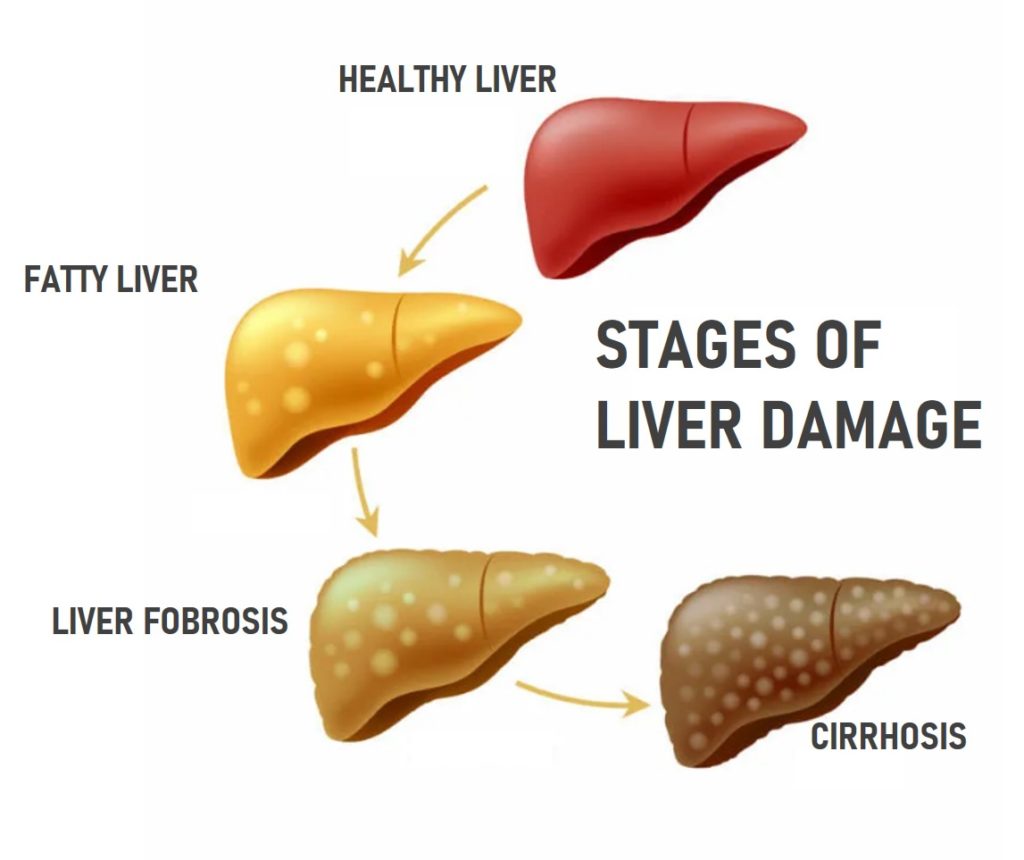
Three Stages of Fatty Liver Disease
The good news is that in most cases, the fatty liver does not cause any significant problems for patients. In the early stages of the disease, when there is no inflammation or swelling, it does not cause any harm.
- Stage 1:around 15-20% of those with fatty liver experience swelling or inflammation in the liver cells, which is called Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)for non-alcoholics and Steatohepatitis in general for both types.
- Stage 2: In some cases, this inflammation leads to scar formation at the site of damage known as fibrosis.
- Stage 3:The liver gradually becomes scared extensively called cirrhosis which can lead to complications like liver failure and hepatic cancer. Fortunately, this is a rare occurrence, with only 8% of people reaching this stage.
Different Stages of Fatty Liver Disease
Prevalence
Fatty liver is prevalent, with almost 30% of the general public suffering from NAFLD. For those with lifestyle-related ailments such as obesity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes, the percentage of people with fatty liver increases to 60%. However, in the early stages of the disease, there are no significant symptoms, except for a dragging sensation or heaviness in the upper right portion of the abdomen in 10-15% of people.
Diagnosis
Early detection is essential for effective treatment. Fortunately, with body checkups like ultrasound, and CT scans (to take images) fatty liver can be diagnosed, even during routine examinations. Blood tests such as liver function, liver biopsy, and Fibroscan(alternate to biopsy and similar to sonography), can help determine whether it is NASH or plain steatosis.
Treatment of Fatty Liver
There are two types of treatment including:
- Lifestyle modification.
- Medical care
Lifestyle modification.
The good news is that fatty liver is curable as this is a lifestyle-related disease.
- Controlling lifestyle-related ailments such as obesity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes can prevent this disease.
- Reducing weight by 5 to 10% can also help control fatty liver.
- A healthy lifestyle that includes 30 minutes of brisk walking, changing food habits to reduce fried and sweet foods, and reducing calorie intake by 30% can protect against lifestyle-related diseases.
Medical Care
Treating underline causes with proper medication for conditions like blood pressure and diabetes. Advice by health care practitioners is important in this respect.
Conclusion
In conclusion, for FATTY LIVER DISEASE (STEATOSIS) we can say:
Prevention is better than cure.
Effective prevention tips include regular exercise or brisk walking. Cut down on carbonated and artificial sweeteners. Try to avoid highly refined food items like bakery bread, pasta, canned foods, and frozen items from supermarkets. Add some greens to your diet including fresh fruits and vegetables. You will get what you give to your body.