Round the globe chest pain or chest discomfort is haunting like a nightmare. Some are experiencing it on one side either left or right, while others have pain on both sides simultaneously. Still, another group exists who are complaining of chest pain in the middle of their chest. For the last one, you can visit my post Causes of Central Chest Pain in the Middle of the Chest. In this blog post, we will be trying to check out left-sided chest pain vs right-sided chest pain. For having a comparison between left-sided and right-sided chest pain an insight into similarities and differences is essential. In addition, we will try to figure out the causes that are leading to chest discomfort on both sides simultaneously.
Structural Insight to Make Left and Right-sided Chest Pain Clear:
As a general rule, core knowledge of layout is mandatory for understanding anything. Similarly, for having a clear concept of Left-sided chest pain vs Right-sided, and to check what can make you hurt on both sides we must have a bird’s eye view of the structures present there. It will make our comparison easier and more absorbable! In these templates, you can have an idea of the structures present in the chest on both sides.
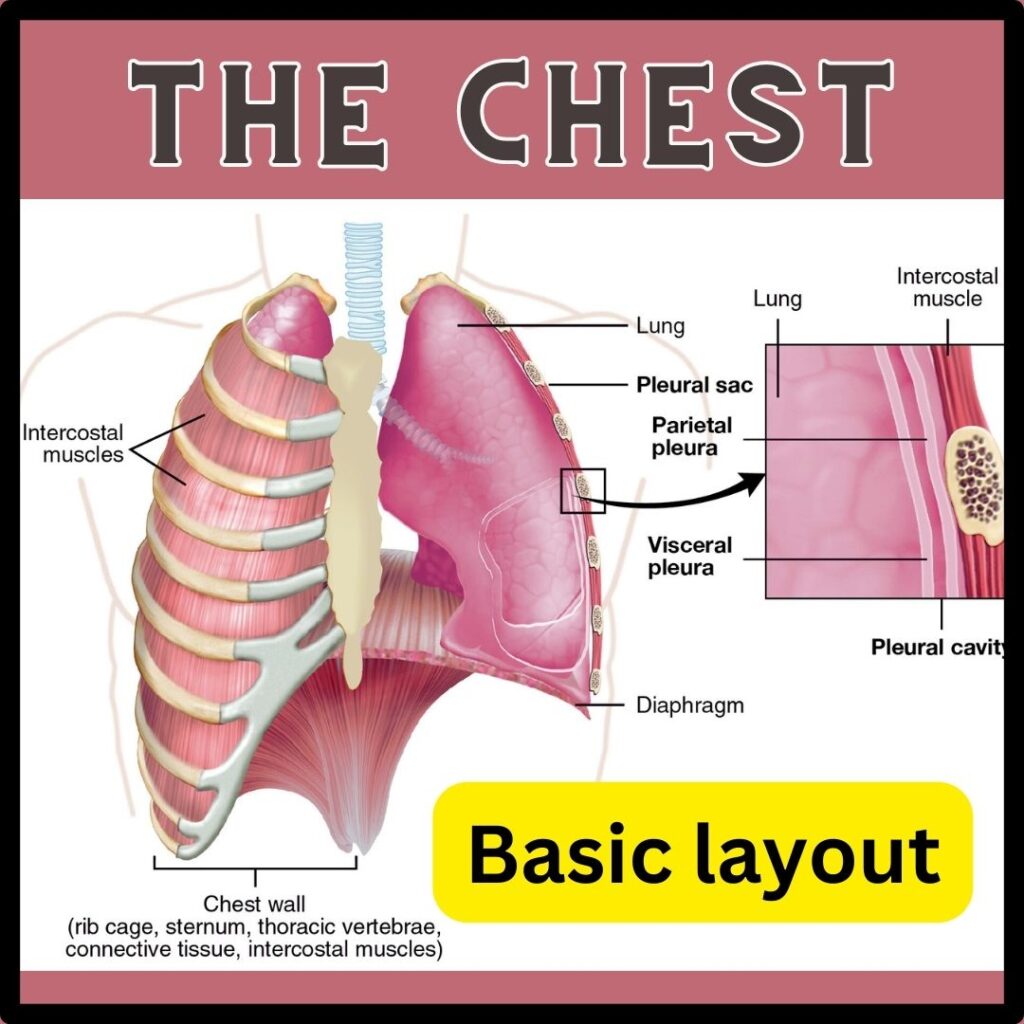
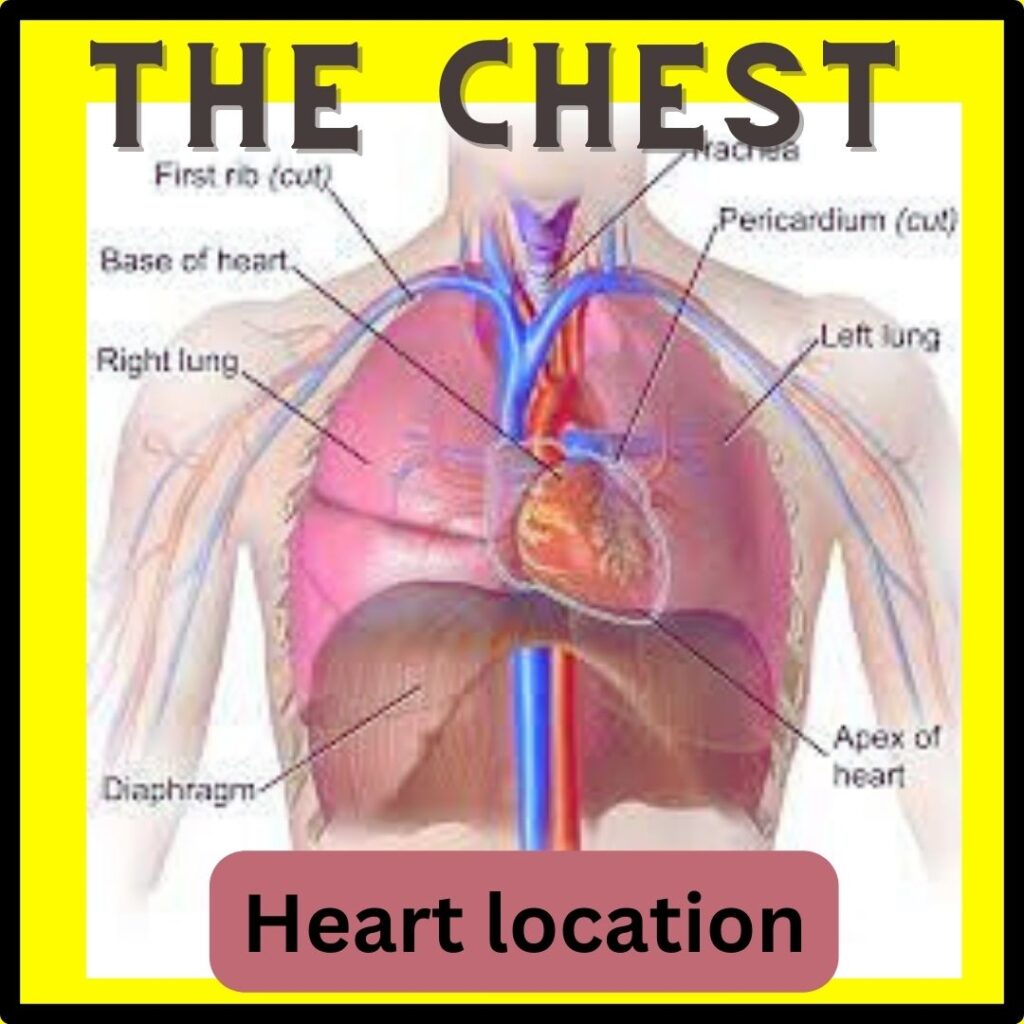
Comparison of Left-sided and Right-Sided Pain in the Chest:
A comparison consists of similarities and differences between certain topics. There are certain common conditions that can bring this discomfort on either side or both sides at the same time. In addition, certain structures cause side-specific chest discomfort.
Common Causes of Left and Right-Sided Chest Pain:
Lung issues
These can lead to either left-sided or right-sided chest pain. These conditions can also be hurting both sides simultaneously. It all depends upon which side of the lung and related vessels or coverings are involved. The major causes include:
- Pulmonary Hypertension, Elevated blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries, which transport blood to the lungs to exchange carbon dioxide for oxygen, can cause blood vessels in the lungs to be narrowed, blocked, and or destroyed. The patient complains of chest pressure or pain, shortness of breath initially with exercising, and eventually even at rest along with other symptoms.
- Pulmonary embolism involves a blood clot arising elsewhere in the body that becomes lodged in and blocked a pulmonary artery within the lung. Along with shortness of breath, individuals with this condition may experience sharp pain that intensifies during inhalation.
- Pneumonia, When the immune system is weakened, it is possible to develop a lung infection. Symptoms of such an infection may include fever, chills, coughing with the presence of mucus, and pain on either side of the chest.
- Pleurisy, and pleuritis, Inflammation or infection of the membranes surrounding the lungs can result in sharp chest pain that worsens with deep breathing or coughing. Additionally, individuals may experience shoulder pain as well.
- Pneumothorax When air enters pleural space (a potential space between layers of pleural membranes that envelop the lungs), it can lead to the collapse of a portion or the entire lung. For the understanding purpose, we can say it is AIR BETWEEN LUNG AND CHEST WALL. This condition can cause sudden onset, sharp pain in the chest along with shortness of breath, and a history of trauma is usually there.
- Lung Cancer causes chest pain that increases in intensity when the patient coughs, laughs, or breath deeply along with coughing up blood or rust-colored sputum (spit or phlegm).
- Asthma, Exposure to allergens or irritants can cause temporary narrowing of the airways, making breathing difficult. This can result in chest tightness, coughing, and wheezing.
- COPD (Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), is a chronic lung and airway disease. In asthma, COPD, and pulmonary hypertension the symptoms are on both sides as both lungs and related structures are affected.
Chest wall conditions:
Some Chest wall conditions can lead to pain on the right or left side of the chest depending on the side involved including:
- Broken ribs, Injuries, or accidents can cause the ribs that protect the chest to fracture, resulting in significant pain, especially when taking deep breaths. This discomfort can last for many weeks.
- Muscular spasms ( may involve smaller intercostal or larger pectoral muscle groups). Muscular spasm due to cold exposure, and overexertion affects both sides. Injuries can lead to tears in the muscles, causing pain, particularly during movement and breathing or coughing. The side of pain may be left, right, or both, and the level of pain may be upper or lower depending on the side and level of muscles involved, respectively. Additionally, individuals may experience swelling and bruising, painful to touch, in the affected area, if there is any injury. Prolonged cough as in certain viral conditions causes chest pain involving the lower chest on both sides as the muscles get exhausted.
- Shingles: Viral in origin can occur anywhere and the culprit agent is the Varicella-zoster virus — the same nagging one that causes chickenpox in childhood. If the chest is involved this virus will lead to a painful strip of vesicles on the involved side. Pain is severe, burning, or tingling.
- Costochondritis should be mentioned here. It is actually considered by doctors as the cause of central chest pain but some patients give a more specific presentation describing it as middle chest pain (to be more specific) slightly right or left of midline. The pain is sharp, increased with breathing, and comes and goes. It can also be on both sides.
Side Specific Causes:
Left-sided Chest Pain vs Right-sided Causes:
The comparison template will make your concept clear about side-specific causes.
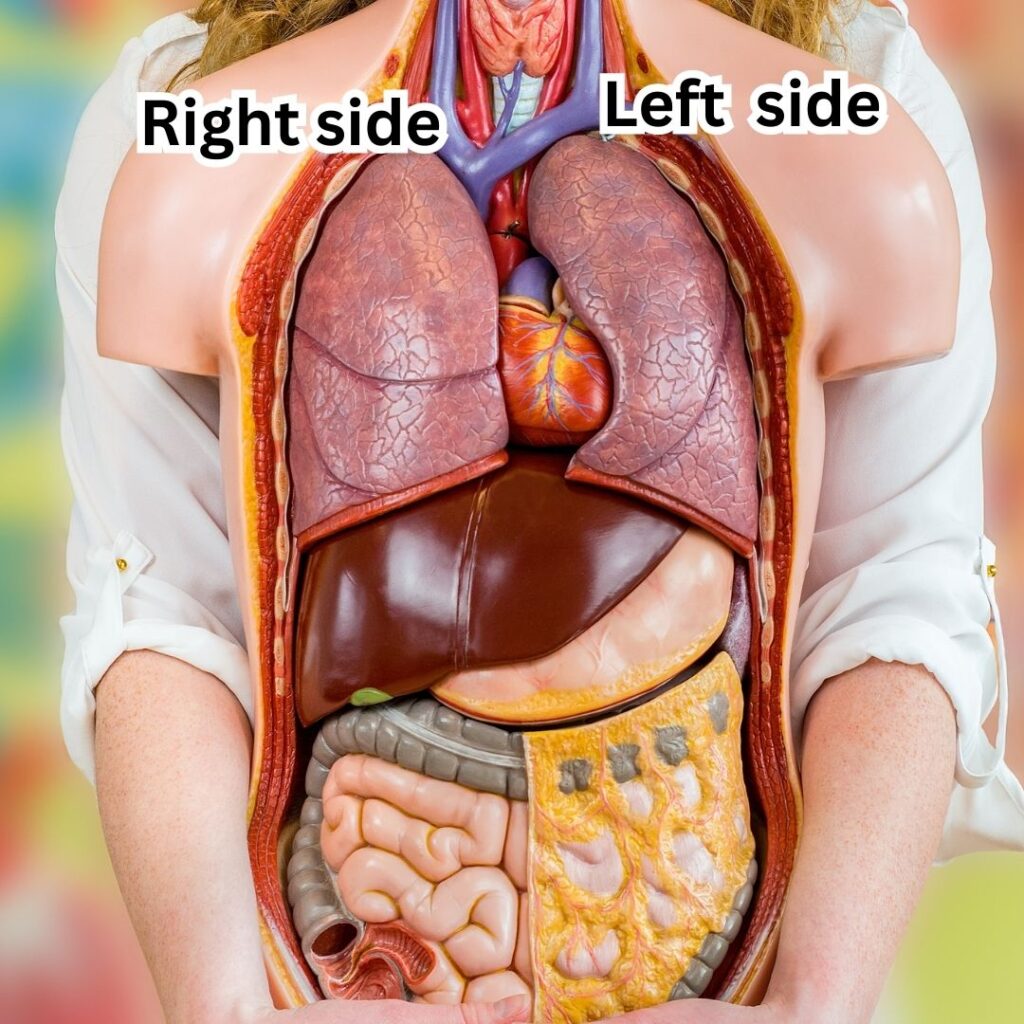
- The heart and related structures cause pain primarily on the left side and sometimes in the central area. Moreover, gastritis and pancreatitis primarily cause tummy pain but the patient can describe it as pain in the lower chest beneath the breastbone in the center or underneath the left lower ribs.
- The liver and gallbladder which are abdominal structures, primarily cause pain in the upper right part of the tummy which can be described by the patient as pain just beneath the right lower ribs or sometimes in the center beneath the breast bone.
Moreover, to have more detailed knowledge visit my post Left _sided chest Pain and right-sided chest pain.
Conclusion:
Left-sided vs right-sided chest pain is not difficult to understand. With brief knowledge of basic structures on the respective sides as well as structures nearby, one can easily compare these causes of chest discomfort.